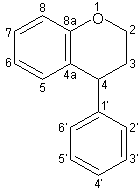
Neoflavonoids are a class of polyphenolic compounds. While flavonoids (in the narrow sense) have the 2-phenylchromen-4-one backbone, neoflavonoids have the 4-phenylchromen backbone with no hydroxyl group substitution at position 2.
Types
Neoflavonoids include 4-arylcoumarins (neoflavones), 4-arylchromanes, dalbergiones and dalbergiquinols.
- Neoflavones are derived from the 4-phenylcoumarin (or 4-aryl-coumarin) backbone (C15H12O2). The first neoflavone isolated from natural sources was calophyllolide from Calophyllum inophyllum seeds (1951). It is also found in the bark and timber of the plant Mesua thwaitesii, endemic to Sri Lanka.
- Neoflavenes possess the 4-phenylchromen backbone (C15H10O2). Dalbergichromene, extracted from the stem-bark and heartwood of Dalbergia sissoo, is an example of such compounds
Other examples
- Coutareagenin (5-hydroxy-7-methoxy-4-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-2H-benzo-1-pyran-2-on) found in Hintonia latiflora
- Dalbergin
- Nivetin isolated from Echinops niveus
See Also
- 3-Phenylcoumarin
References
External links
The dictionary definition of neoflavonoid at Wiktionary